Proxy vs. VPN vs. Antidetect Browser: Which One Should You Choose?
Take a Quick Look
Proxy, VPN, or Anti-Detect Browser—which is best for privacy and multi-account management? This guide compares them to help you choose the right tool.
Have you ever faced account suspensions, privacy breaches, or geo-restricted access while browsing the web? If so, you're not alone. As online privacy and security threats continue to grow, choosing the right tool to protect your digital identity has never been more important. In this article, we'll dive into the world of anti-detect browsers, VPNs, and proxies—three popular tools used for online privacy, security, and account management.
The question is: Which one is best for you? This guide will help you understand the key differences among anti-detect browsers, VPNs, and proxies, analyze their core features, and provide practical advice on which solution suits your specific needs.
Core Features Comparison: Proxy vs. VPN vs. Antidetect Browser
To begin with, let's break down the essential features of anti-detect browsers, VPNs, and proxies in a quick, easy-to-read table:
|
Feature |
Anti-Detect Browsers | VPN | Proxy |
| Mask IP Address | ✅Use with Proxy | ✅ | ✅ |
| Modify Browser Fingerprint | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Encrypt Traffic | ✅depends on proxy type | ✅ | ✅depends on proxy type |
| Prevent Account Linking | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Bypass Geo-restrictions | ✅Use with Proxy | ✅ | ✅ |
| Use Cases | Multi-account management, Ads, Affiliate Marketing, eCommerce and more. | Privacy, Streaming, Remote work | Data scraping, Anonymous browsing, SEO monitoring |
| Ease of Use | Medium to High | High | Medium |
| Security | High | High | Medium |
Now that we've compared the core features of proxy vs. VPN vs. antidetect browser, let's dive deeper into each one.
Pros and Cons Analysis: Proxy vs. VPN vs. Antidetect Browser
When choosing a tool for online privacy, security, or multi-account management, it's essential to understand the strengths and weaknesses of each option. Below, we break down the pros and cons of proxies, VPNs, and anti-detect browsers to help you make an informed decision.
1. Proxy
A proxy acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet, masking your real IP address and routing your traffic through a different server. When you access a website through a proxy, your request is first sent to the proxy server, which then forwards it to the destination using a different IP address. The website's response is sent back through the proxy before reaching you, keeping your actual IP hidden.
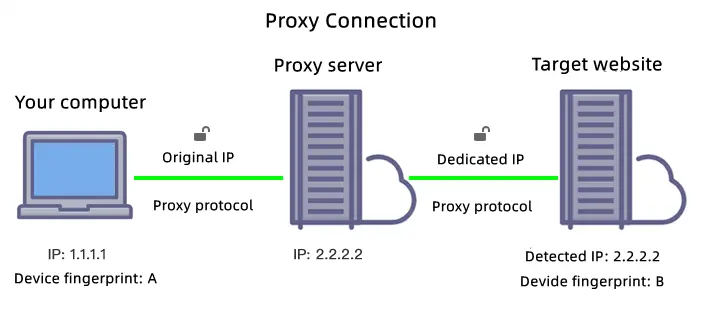
The Pros of Proxies
- Anonymous Browsing: Proxies hide your real IP address, allowing you to browse the internet anonymously.
- Cost-Effective: Proxies are typically cheaper than VPNs and anti-detect browsers, making them a good option for those on a tight budget.
- Flexible Location: You can choose proxies from different locations around the world, enabling you to simulate browsing from any country.
- Lightweight and Fast: Since proxies do not encrypt traffic, they offer faster speeds compared to VPNs. However, the speed can vary depending on the type of proxy, the quality of the proxy server, and the network conditions. For instance, residential proxies tend to offer better performance than data center proxies but come at a higher cost.
The Cons Proxies
- No Encryption: Unlike VPNs, proxies do not encrypt your traffic. This leaves your data vulnerable to interception, making it unsuitable for users who prioritize security.
- Connection Stability: Some proxies vs VPN comparisons show VPNs are more stable than proxies, especially free or low-quality proxies.
- Limited Multi-Account Management: Like VPNs, proxies do not modify your browser fingerprint, making them less effective for preventing account linking or managing multiple accounts.
2. VPN (Virtual Private Network)
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) works by routing your internet traffic through a remote server, effectively masking your IP address and encrypting your data. This provides a secure connection, making it difficult for third parties such as hackers or your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to monitor your online activities.
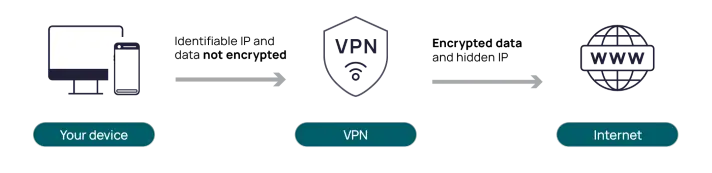
The Pros of VPNs
- Encrypts Traffic: Unlike proxies, VPNs encrypt your internet traffic, making it unreadable to anyone who might intercept it. This is ideal for protecting your online activities from hackers, your ISP, or any other third parties.
- Bypasses Geo-Restrictions: VPNs allow access to geo-blocked content, such as Netflix, Hulu, and YouTube.
- Easy to Use: Most VPNs offer one-click connection, making them accessible even to those with limited technical expertise.
The Cons of VPNs
- Reduced Speed: VPNs can slow down your internet connection due to the encryption process and rerouting through remote servers.
- Limited Multi-Account Management: VPNs vs proxies both fail to modify browser fingerprints, making them less effective for managing multiple accounts.
- Certain Sites Block VPNs: Some websites, particularly banking sites or websites that deal with sensitive information, may block or restrict access from VPNs.
3. Anti-Detect Browsers
In everyday browsing, fingerprint tracking enables personalized ads, while stricter platforms may still detect and link multiple accounts—even after clearing cookies or using a VPN—leading to bans or restrictions.
Anti-Detect Browsers help prevent this by modifying browser fingerprints—unique identifiers based on parameters like user-agent, screen resolution, time zone, installed fonts, and plugins. Unlike regular browsers, which reveal these details to websites, anti-detect browsers let users change them to avoid tracking and account linking. This means even if your IP changes, platforms won't easily detect or associate your accounts.
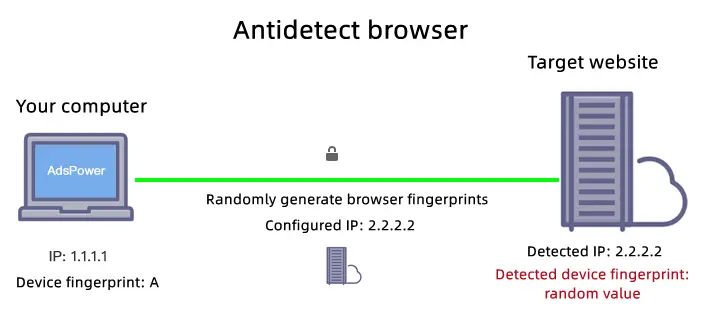
The Pros of Anti-Detect Browsers
- Multi-Account Management: These browsers are perfect for managing multiple accounts on virtually any online platform. They provide the anonymity and control you need to handle several accounts without the risk of account bans or suspensions.
- Avoids Account Linking & Bans: By altering fingerprint elements such as Canvas and WebGL hashes, anti-detect browsers prevent platforms from associating accounts, significantly reducing ban risks.
- Highly Customizable: You can tweak your browser fingerprint (like browser type, screen resolution, and language) to suit the specific requirements of each platform.
- Stronger Anonymity: Unlike VPNs and proxies, which primarily mask your IP address, anti-detect browsers also modify your browser fingerprint, offering a deeper level of protection against tracking.
Seamless Team Collaboration: Some advanced anti-detect browsers, like AdsPower, provide team management features for secure, shared multi-account operations.
The Cons of Anti-Detect Browsers
- Best Used with a Proxy: While anti-detect browsers excel at modifying browser fingerprints, they work best when paired with a proxy to ensure complete IP protection. This combination enhances anonymity and security for seamless multi-account management.
- Higher Cost: Anti-detect browsers tend to be more expensive than VPNs and proxies due to their advanced features and customizability. But AdsPower changes that! With plans starting at just $5.4/month when billed annually, you get a powerful yet affordable solution—plus, you can try it for free!
When to Use a Proxy, VPN, or Anti-Detect Browser?
Proxies, VPNs, and anti-detect browsers all enhance anonymity and protect online privacy. Each tool has its own set of benefits, so choosing the right one depends on your specific needs.
When to Use a Proxy?
- You need to scrape data or perform SEO monitoring without revealing your real IP address.
- You're looking for a budget-friendly solution that allows you to access content from different geographical locations.
- You don't need encryption, but rather just an anonymous browsing experience.
When to Use a VPN?
- You want to protect your privacy and encrypt your internet traffic to prevent hackers or ISPs from monitoring your activity.
- You need to access geo-restricted content, such as streaming services or websites blocked in your region.
- You need a simple, easy-to-use tool to secure your online activities.
When to Use Anti-Detect Browsers?
If you're looking for the most comprehensive solution, an anti-detect browser is the best choice. AdsPower, for example, goes beyond fingerprint customization by offering team collaboration, multi-account management, RPA automation, and more.
You should especially consider using an anti-detect browser when:
- You need to manage multiple accounts without the risk of being flagged.
- Preventing account linking or bans across platforms is your top priority.
- You want to modify your browser fingerprint for enhanced anonymity and security.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the difference between a Proxy and VPN?
A proxy only hides your IP address and does not encrypt traffic, while a VPN masks your IP and encrypts your traffic, making it the better option for users concerned with privacy and security.
Which tool is best for advertising and social media accounts?
For Facebook, Google Ads, eCommerce, or any multi-account activity, anti-detect browsers are the most suitable. The most secure setup is to assign each account to a unique fingerprint browser profile paired with a dedicated proxy, ensuring maximum privacy and minimizing the risk of account linking.
Final Thoughts
Whether you're an advertiser, an eCommerce seller, or just someone concerned about online privacy, understanding the differences between anti-detect browsers, VPNs, and proxies is crucial to making an informed decision. AdsPower offers the most powerful solution for multi-account management, helping you secure your online identity while managing several accounts across platforms.
Don't wait—try AdsPower today and experience seamless, secure account management like never before!

People Also Read
- Nutra Affiliate Marketing Strategies – Expert Guide for 2025
- Simple Fixes for Common AdsPower Extension Errors and Failures
- Traffic Arbitrage for Beginners: A Step-by-Step Guide to Profitable Campaigns in 2025
- How to Bulk Update Proxies in AdsPower
- The Best Email Affiliate Marketing Strategies for Higher Conversions

