Web Tracking: The Digital Footprints We Leave Behind
Take a Quick Look
Web tracking can expose your personal data, but with the right tools and strategies, you can safeguard your privacy and browse securely.
Have you ever had a similar experience: you're chatting with a friend about getting a new pair of running shoes, and minutes later, your social media feed is flooded with ads for the exact brand you mentioned. Creepy, right? While we've all come to love the convenience of our digital world, something is unsettling happening behind the scenes.
A shocking new report reveals that websites are tracking us with over 38 billion data collection events recorded this year alone. That's more than a million attempts to track your online activities daily. The risks to our privacy and security have become increasingly alarming.

In this blog, we'll dive into the intricacies of web tracking, its methods, dangers, and actionable steps to safeguard your digital footprint.
What Is Website Tracking?
Website tracking, or web tracking, refers to the practice of collecting and analyzing data about a user’s online activity. This is often done by websites and third-party entities to understand user behavior, personalize content, serve targeted ads, or enhance user experiences.
Tracking can involve collecting various types of information, including browsing history, search queries, location data, device information, and even the amount of time spent on a page. While some tracking helps improve website functionality, such as remembering login details, others raise significant privacy concerns.
How Does Web Tracking Work: Examples of Online Tracking
Cookies
One of the most common tracking methods is cookie tracking, which are small text files stored on your device by websites. Cookies help websites remember your preferences, login details, and browsing history. For example, if you log into an e-commerce site, cookies can remember your shopping cart items, making it easier for you to continue browsing without losing your selections.
They come in several forms
-
First-party cookies: Set by the website you're visiting
-
Third-party cookies: Placed by external services, often for advertising purposes
-
Zombie cookies: Self-regenerating cookies that persist even after deletion
While cookies can raise privacy concerns by potentially exposing your online activities, they also serve as critical markers for websites and platforms to verify user authenticity. Blank-slate cookies can sometimes trigger suspicion and lead to accounts being flagged as fraudulent.
Looking to keep your privacy intact while maintaining legitimate-looking accounts? Consider using a cookie robot that offers a robust solution for managing your digital footprint effectively.
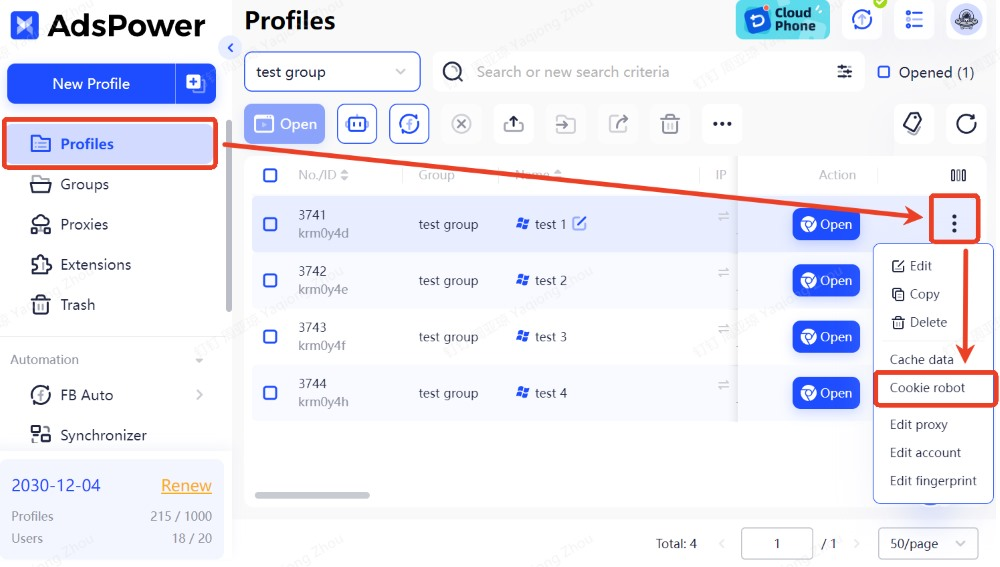
Pixel Tags
Pixel tags, also known as web beacons or tracking pixels, are small, invisible graphics embedded in web pages or emails. These tags send information back to the server when they are loaded, tracking user activity such as page views, clicks, or email opens. Marketers often use pixel tags for targeted advertising and retargeting campaigns. For instance, if you visit a site that sells shoes, a pixel might track your visit and then show you ads for those same shoes across other sites you visit.
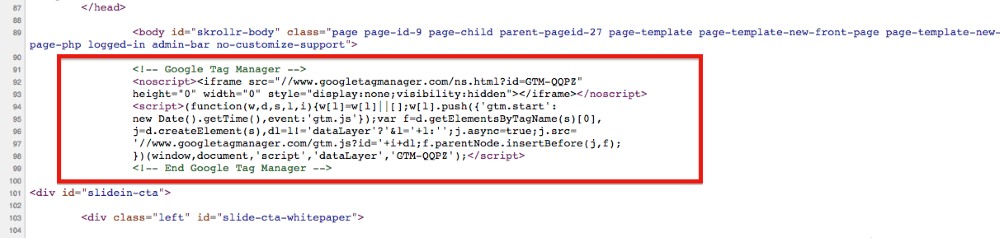
This is what a tag looks like in the source code of a page.
Browser Fingerprinting
Browser fingerprinting is a method that collects unique data points about your device and browser configuration, such as the type of browser, operating system, screen resolution, installed plugins, and even font settings. Unlike cookies, fingerprinting does not require the user’s consent to be effective. This method creates a unique identifier for each device and can track users across multiple sessions.
But does this mean browser fingerprinting is unavoidable? Not necessarily. There are tools called antidetect browsers - think of them as your digital disguise kit. One powerful solution is AdsPower, which lets you create new browser fingerprints that look completely natural on websites.
IP Address Tracking
Every device connected to the internet has a unique IP address. Websites can track your IP address to identify your geographic location, the device you're using, and the websites you visit. While this data alone may not provide specific user details, it helps businesses target you with region-specific ads and content. For example, if you're located in New York, an online retailer may show you different products than someone browsing from California.
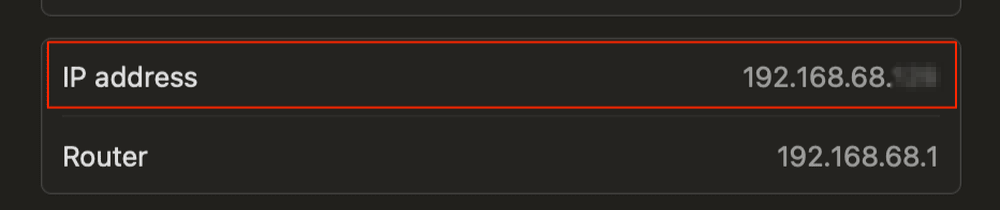
Wondering how to hide your IP address? Here are 7 effective ways!
Session Tracking
Session tracking monitors your activity during a single visit to a website. This method keeps track of pages you visit, how long you stay on each page, and what actions you take (e.g., clicking buttons, submitting forms). Session tracking is often used for analyzing user behavior on a website, determining which pages are most popular, and improving navigation.
Cross-Site Tracking
Cross-site tracking is the practice of tracking users across multiple websites or apps. This is typically achieved through third-party cookies or other tracking technologies embedded by advertising networks. For instance, when you visit a news website and see ads for a hotel, and later see the same hotel ads on a social media platform, that is cross-site tracking at work. Advertising networks collect and share this data to serve you targeted ads based on your browsing history.
The Hidden Dangers of Web Tracking
While web tracking can enhance online experiences, it also poses significant risks:
1. Loss of Privacy
Track web activity often occurs without users’ explicit consent, leading to a lack of transparency. This has sparked debates around digital privacy rights. For instance, tracking can reveal sensitive information such as health conditions or political affiliations.
2. Data Breaches
Collected data is often stored in vast databases that can become targets for cyberattacks. High-profile breaches, such as the 2021 LinkedIn data scrape, exposed the personal information of millions of users.
3. Manipulative Practices
Advertisers and platforms may exploit tracking data to manipulate user behavior. For example, personalized ads can reinforce unhealthy habits or influence political opinions.
4. Increased Vulnerability to Cyberattacks
The data collected through web tracking can also become a target for hackers. Breaches in ad networks or tracking systems can expose user data to malicious actors, who might exploit it for phishing attacks, identity theft, or financial fraud.
Effective Ways to Stop or Limit Web Tracking
Protecting yourself from web tracking doesn't require technical expertise. Here are some practical methods:
1. Use Privacy Tools: The Safest Way
Antidetect browsers like AdsPower enable anonymous browsing by masking real browser fingerprints and bypassing tracking technologies. But AdsPower offers much more than just online privacy protection.
-
Secure Account Management: Manage multiple accounts without risking suspensions or bans caused by account linking.
-
Advanced Fingerprint Verification: AdsPower's browser fingerprints pass all major fingerprint detection tools - You can easily verify their authenticity and security using BrowserScan's free checker tool.
-
Enhanced Efficiency: Make use of features like Multi-Window Synchronizer & RPA automation to streamline tasks and boost productivity.
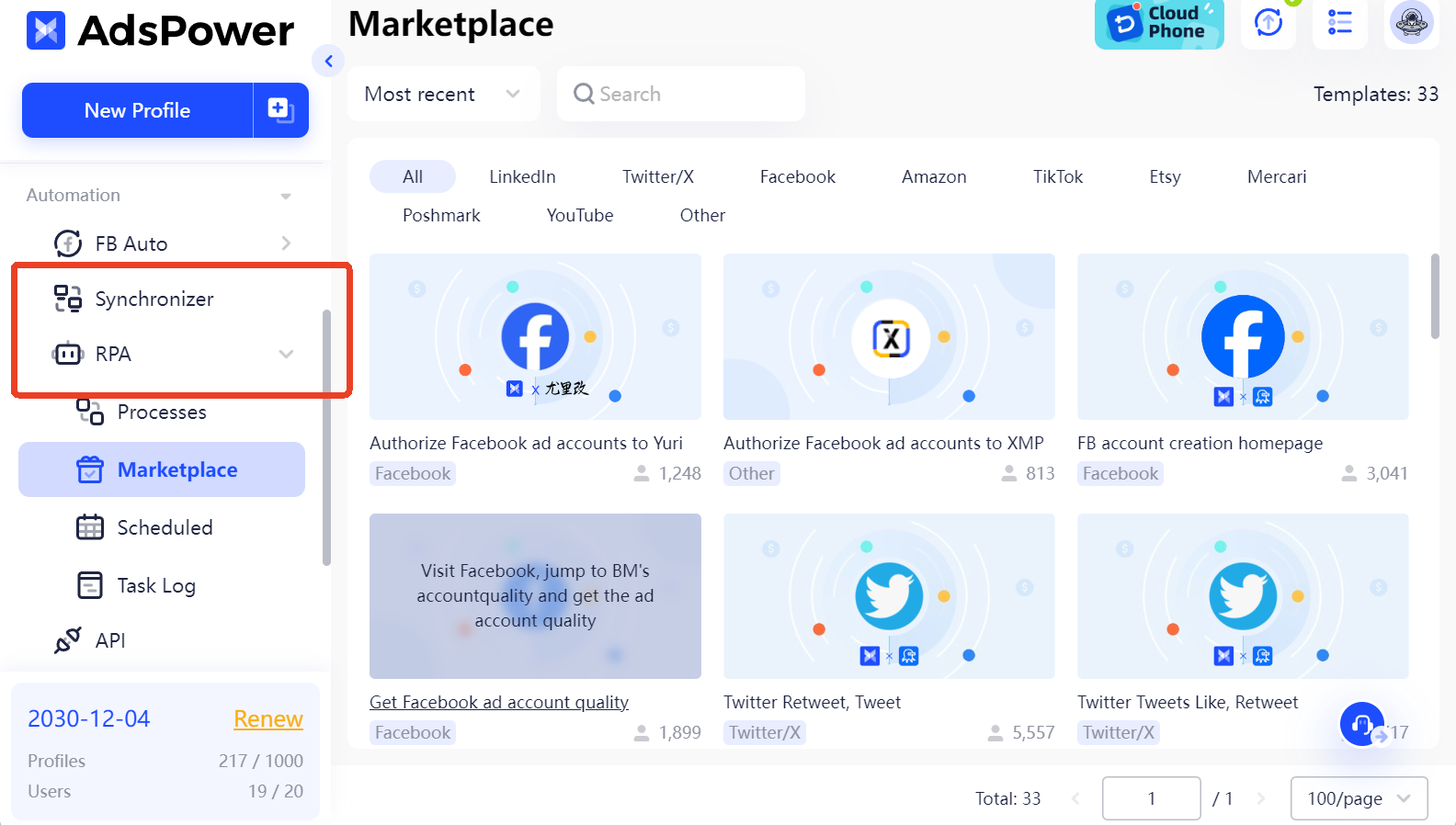
-
Profit Maximization: Whether you're in affiliate marketing, ticket reselling, or cryptocurrency trading, AdsPower helps you scale operations and maximize earnings effortlessly.
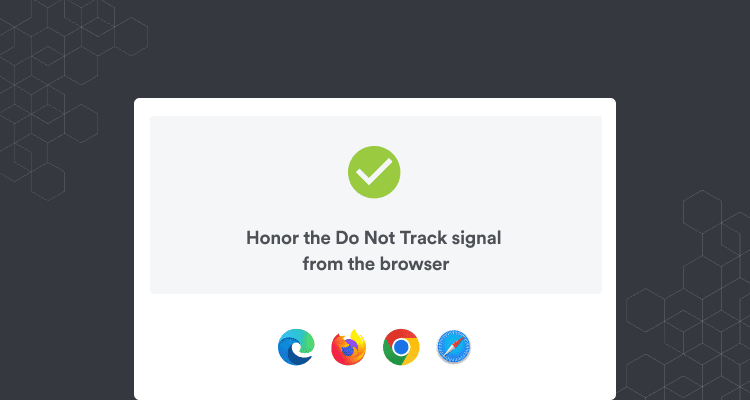
2. Enable Do Not Track
Although not universally respected, enabling the “Do Not Track” setting in your browser is a good starting step.
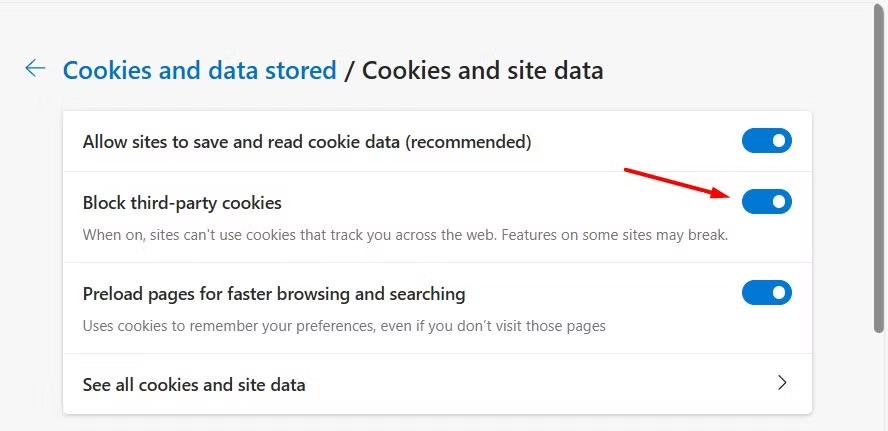
3. Regularly Clear Cookies
Manually deleting cookies or setting your browser to clear them after each session can reduce tracking. Alternatively, use "incognito" or "private browsing" modes.
Tip: Combine this with disabling third-party cookies in your browser settings for stronger protection.
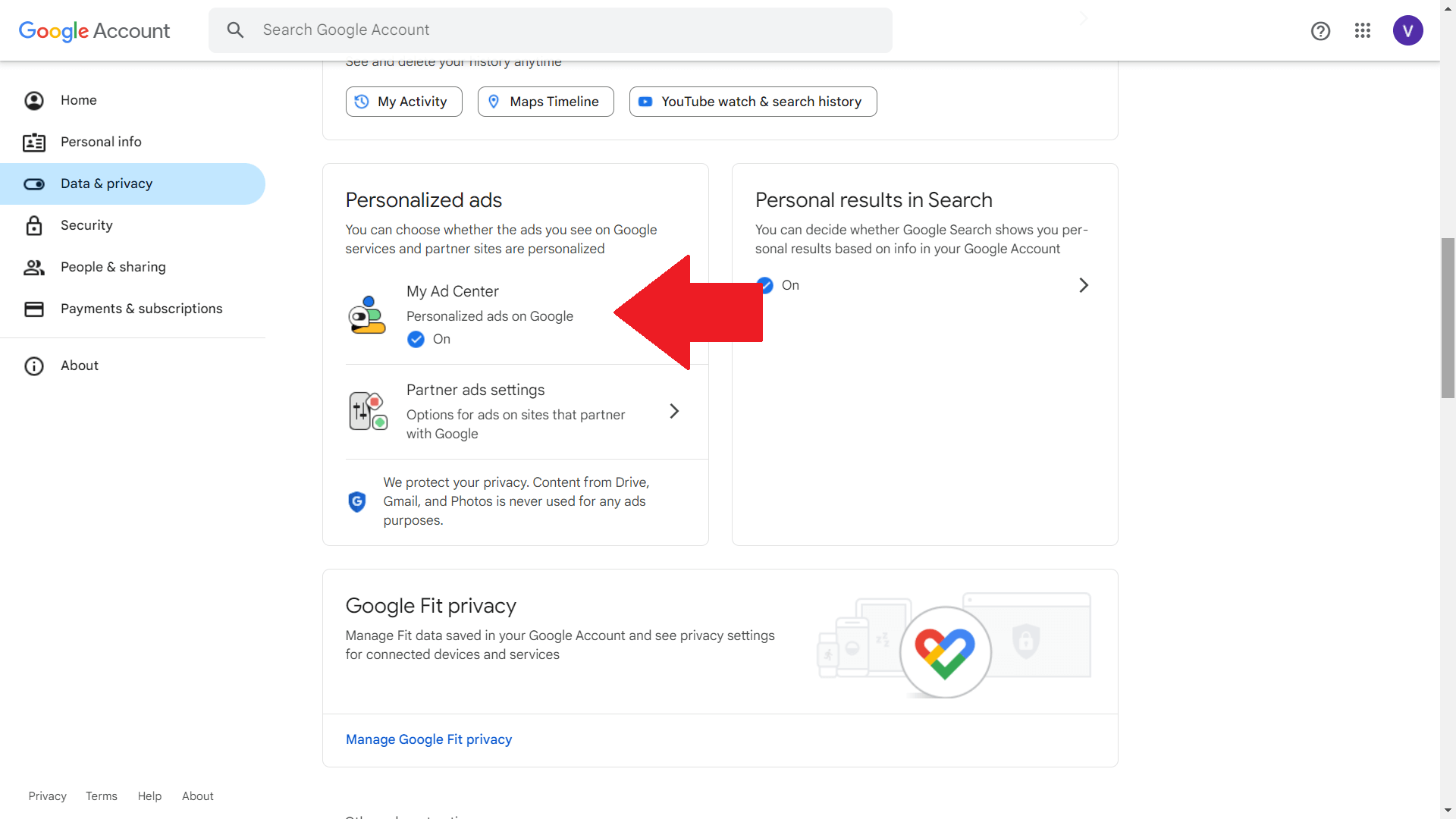
4. Opt Out of Personalized Ads
Platforms like Google and Facebook offer settings to disable ad personalization. While this won’t stop tracking entirely, it reduces the data used for targeting.
How-To: Visit Google's Ad Settings or Facebook's Ad Preferences to manage your preferences.
5. Install Anti-Tracking Extensions
Tools like Privacy Badger and uBlock Origin detect and block trackers in real time. These extensions are easy to install and work across most browsers.
6. Leverage VPNs
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) masks your IP address, making it harder for trackers to identify your location and device. However, it's crucial to choose a reliable VPN provider. Avoid free VPNs, as they may compromise your data security rather than protect it.
FAQs
Q1: Can I Completely Stop Web Tracking?
It is nearly impossible to eliminate tracking entirely due to advanced techniques like fingerprinting. However, using tools like privacy-focused browsers and anti-tracking extensions can significantly reduce it.
Q2: Is Incognito Mode Enough to Stop Tracking?
No, incognito mode only prevents your browsing history from being saved on your device. It does not block trackers or hide your IP address from websites.
Q3: Are All Cookies Harmful?
Not necessarily. First-party cookies improve the user experience by remembering preferences, while third-party cookies are often used for invasive tracking.
Q4: Does Website Tracking Violate The Law?
Website tracking itself isn’t illegal, but practices must comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA, which require user consent and transparency.
Conclusion
Website tracking is a double-edged sword: while it can enhance online experiences, it also poses significant privacy risks. But armed with the insights from this guide, you're now better equipped to take control of your digital footprint while enjoying the conveniences of the modern web.

People Also Read
- How to Download Reddit Videos in 2026: MP4, GIFs, and Images Made Easy

How to Download Reddit Videos in 2026: MP4, GIFs, and Images Made Easy
Learn how to easily and safely download Reddit videos, GIFs, and images in 2026. Step-by-step methods, troubleshooting tips, and best practices includ
- How Do You Make Money on Twitch in 2026? (Complete Guide)

How Do You Make Money on Twitch in 2026? (Complete Guide)
Learn how to make money on Twitch in 2026 with updated monetization methods, viewer tips, income strategies, and tools to help beginners and streamers
- What Is RSOC Search Arbitrage? A Clear Guide to RSOC vs AFD Feeds

What Is RSOC Search Arbitrage? A Clear Guide to RSOC vs AFD Feeds
RSOC vs AFD explained. Learn what RSOC search arbitrage is, how Google RSOC feed and AFD ads work, and which model fits your traffic.
- How to Warm Up X (Twitter) Accounts Safely: A Complete Guide to Using a Cookie Bot

How to Warm Up X (Twitter) Accounts Safely: A Complete Guide to Using a Cookie Bot
Learn how to use a cookie bot to warm up new X accounts safely. Reduce bans, build trust, and automate account preparation with AdsPower's cookie bot.
- How to Access Kickass Torrents Safely: Get Kickass Torrent Site Unblocked

How to Access Kickass Torrents Safely: Get Kickass Torrent Site Unblocked
Safely access Kickass Torrents in 2025 with secure tools, trusted mirrors, and step-by-step methods to unblock, download, and avoid malware or risks.



